回顾对象的内容
使用Type或inferface描述对象类型
type可以理解为集合,学名叫类型别名Type Alias,用于给其他类型取名字;interface为声明接口,interface可以描述对象的属性(declare the shapes of objects)。
type Person = {
name: string
}
type Person = {
name: string, age: string
} | {
name: string, age: number
} | {
name: string, gender: string
} | {
name: string, gender: number
}
// ....
interface Person {
name: string
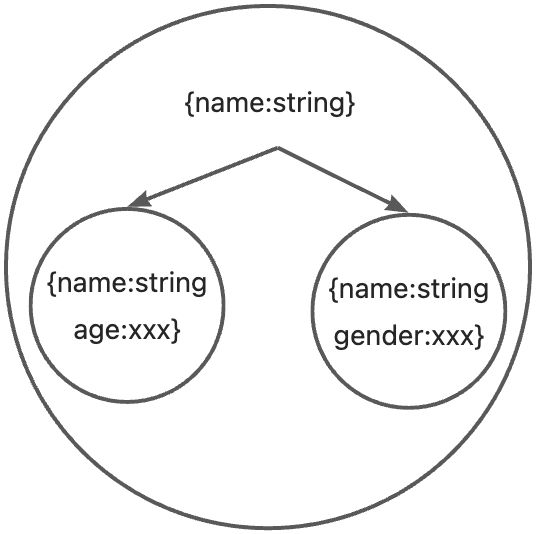
}如左边案例所示,可以看出属性越多,集合越小。
 ### 索引签名与映射类型
### 索引签名与映射类型
索引签名(Index Signature)可以和普通的属性一起使用。
type Hash = {
[k: string]: unknown
length: number
}
type List = {
[k: number]: unknown
length: number
}映射类型(Mapped Type),无法添加属性,独占这个花括号,多用于范型。
type Hash = {
[k in string]: unknown
}
type List = {
[k in number]: unknown
}问号是否可选
interface InputProps {
defaultValue?: string
value?: string
onChange?: () => void
}
// 举例做到二选一
// 1.用了 defaultValue 就不能用 value
// 2.用了 value 就必须用 onChange
// 在不用范型的前提下,达到条件,但还是有问题
type InputProps = {
defaultValue?: string
value?: undefined
onChange?: () => undefined
} | {
defaultValue?: undefined
value?: string
onChange?: () => void
}readonly表示只读
readonly表示只读,不能写。但有局限性,属性里面的值不会进行限制。
interface User {
readonly id: number
readonly name: string
readonly scores: number[]
age?: number
}
const u: User = {
id: 1,
name: 'frank'
scores: [87, 52]
}
u.id = 2
// ^-- Cannot assgin to 'id' because
// it is a read-only property.ts(2540)
u.scores[0] = 100
// 不报错描述对象总结:
- type 或 interface
- 索引签名 和 映射类型
- 问号表示可选
- readonly表示只读
深入函数的内容
函数的语法
对象的语法全部适用于函数。JS声明函数的方法和TS声明函数的方法有点不同,具体举例如下所示。
JS声明函数的方法
// js function
function functionName() { // body }
const functionName = functionName() { // body }
const functionName = () => { // body }
const f4 = new Function('a','b','return a + b')TS五种声明函数的方法(生成器和异步函数除外)
// 第一种:先写类型在赋值
type F1 = (a: number, b: number) => number
const f1: F1 = (a,b) => a + b
// 第二种:先实现箭头函数,再获取类型
const f2 = (a: number, b: number): number => {
return a + b
}
type F2 = typeof f2
// 第三种写法:先实现普通函数,再获取类型
function f3 (this: unknown, a: number, b: number): number {
return a + b
}
type F3 = typeof f3
// 第四种:先实现匿名普通函数,再获取类型
const f4 = function (this: unknown, a: number, b: number): number {
return a + b
}
type F4 = typeof f4
// 第五种:没人写
const f5 = new Function('a','b', 'return a + b')
type F5 = typeof f5两种特殊函数
- 构造函数(待完善)
- 类型谓词
类型谓词,做类型联合的时候使用,用于类型收窄
type Person = {
name: string
}
type Animal = {
xxx: string
}
type A = Person | Animal
function f1(a: A) {
if (isPerson(a)) {
a.name
} else {
a.xxx
}
}
function isPerson (x: Person | Animal):x is Person {
return 'name' in x
}
const isPerson2 = (x: Person | Animal) => x is Person => {
return 'name' in x
}可选参数
可选参数只需要在属性的冒号前添加问号。可选参数必须放在必选参数后面。因为无法做到第一个可选,第三个可选,必选参数不可以再可选参数后面。
type AddEventListener = (eventType: string, fn: unknown, useCapture?: boolean) => void
const addEventListener: AddEventListener = (eventType,fn,useCapture) => {
// body
// 若是useCapture没有传入
if(useCapture === undefined) = {
// ...
}
}
addEventListener('click',() => {})参数默认值
参数默认值其实是js的知识,即只要在参数后面添加**=**然后加默认值。举例函数的第三个参数若要设置默认值,如下所示。
type AddEventListener = (eventType: string, fn: unknown, useCapture?: boolean) => void
// 使用时候设置默认值
const addEventListener: AddEventListener = (eventType,fn,useCapture = false) => {
// body
// 若是useCapture没有传入
}
// 偷懒的方法, ts会自动去推断类型
const addEventListener = (eventType: string, fn: () => void, useCapture = false) => {
// body
}
addEventListener('click',() => {})
// 若参数为对象时
const fn1 = (config = {a:[],b:'x',c:'x'}) => {
// ^ never[]
// body
}
// 或声明config类型
type Config = { a: string[], b: string, c: string }
const fn2 = (config:Config = {a:[],b:'x',c:'x'}) => {}
// 或用断言
const fn3 = (config = {a:[],b:'x',c:'x'} as Config) => {}参数也是函数
type AddEventListener = (
eventType: string,
fn: (e: Event)=> void,
useCapture?: boolean) => void
const addEventListener: AddEventListener = (eventType,fn,useCapture = false) => {
// 浏览器的代码 伪代码
const event: Event = {} as any
const element: Element = {} as any
fn.call(element, event)
// body
}返回值也是一个函数
// 返回值为函数
function createAdd(n:number) {
return function (m:number) {
return m + n
}
}
// 先写类型
// type F = (n:number) => ((m: number) => number)
type E = (n: number) => (m: number) => number
const createAdd: E => n => m => m + n
const add = createAdd(6)
console.log(add(5))
export {}重载
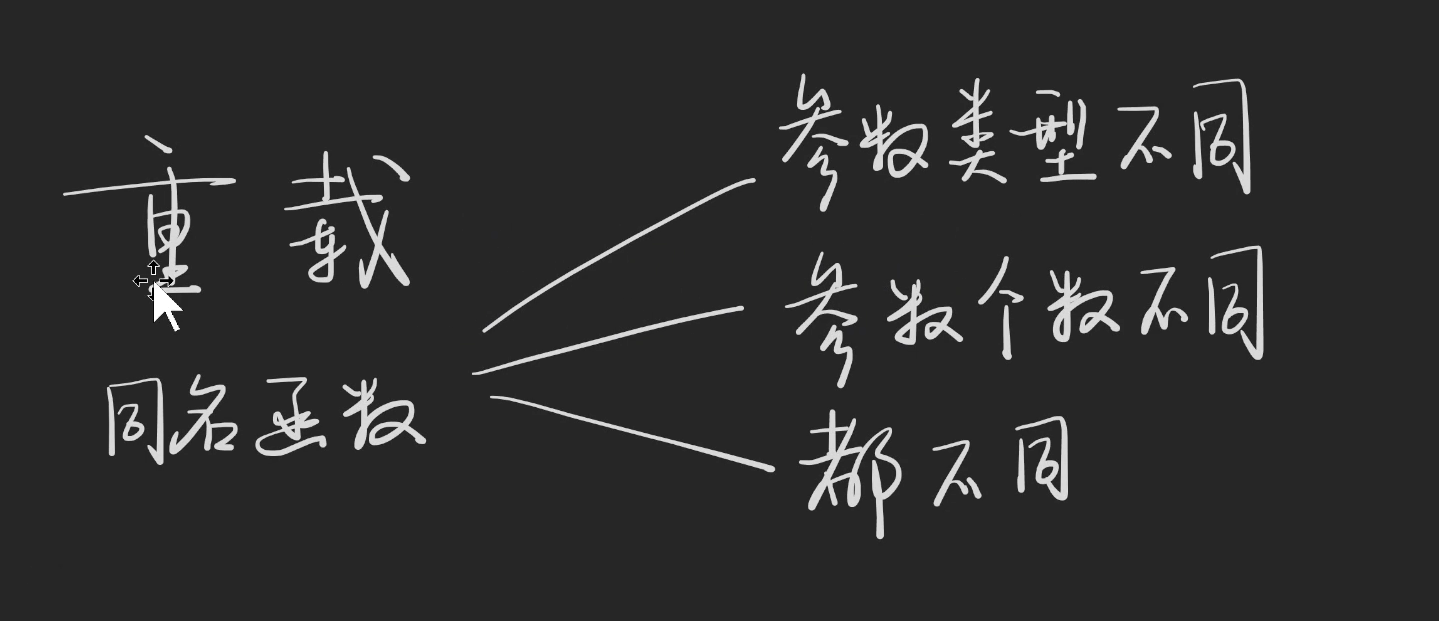
重载就是同名函数,可以接受参数类型不同、参数个数不同、都不同。即满足右边的三种情况,详细内容见TS官网的链接。重载能不用就不用,除非折磨自己。重载适合牛逼的库比如 JQuery 不想取多个名字,也可以通过重载对axios进行二次分装。
// 重载
// 案例一
type Print = (n: string | number) => void
type Print2 = (a: string | number, b?: string | number) => void
type Print3 = (a: boolean, b?: string | number) => void
function print(n: string | number): void
function print(a: boolean, b: string | number): void
function print(a: (string | number) | boolean, b?: string | number): void {
if (typeof a === 'boolean') {
if (b) {
console.log(a, b)
} else {
console.log(a)
}
} else {
// a
}
}
// java 的重载 名字相同 同名不同参,与返回类型无关
// 案例二 可以看ts官网案例
// ts的重载是可以使用联合类型的 与 java的重载不同
// 重载只描述参数的,对于返回值并不管
// function createDate(n: number): void; //场景1
// function createDate(year: number, month: number, date: number): void; //场景2
// // 实现签名 只需要在逻辑上兼容上面的情况
// function createDate(x: number, y?: number, z?: number): void {
//
// }
// 两种最大的集合
function createDate(n: number): Date; //场景1
function createDate(year: number, month: number, date: number): Date; //场景2
// 实现签名 只需要在逻辑上兼容上面的情况
//
function createDate(x: number, y?: number, z?: number): Date {
if (z !== undefined && y !== undefined) {
// year month date
// createDate(2011, undefined, 1)
return new Date(x, y, z)
}
if (x !== undefined && y !== undefined && z !== undefined) {
// createDate(2011, 1, undefined)
// n
return new Date(x)
}
// 防御型编程
throw new Error('参数错误')
}
// 还不如直接写两个函数
function createDateFormNumber(n: number): Date {
return new Date(n)
}
function createDateFormYMD(x: number, y: number, z: number): Date {
return new Date(x, y, z)
}
// 上述那种重载适合牛逼的库比如 JQuery 不想取多个名字 二次分装axios
// $div = $('#id')
// $div = $(div)
// $div = $('<div>hi</div>')
// $div = $(document)
// $div = $(document.body)
// $div = $(window)
// 请求方式
// js ajax
const xhr = new XMLHttpRequest()
xhr.open('post', '/xxx')
xhr.onreadystatechange = () => {
if (xhr.readyState) {
}
}
xhr.setRequestHeader('Content-Type', 'application/json')
xhr.send(JSON.stringify({xx: 'baizhe'}))
// Fetch
// fetch()
//可以在控制台发出fetch请求
// Axios指定this类型
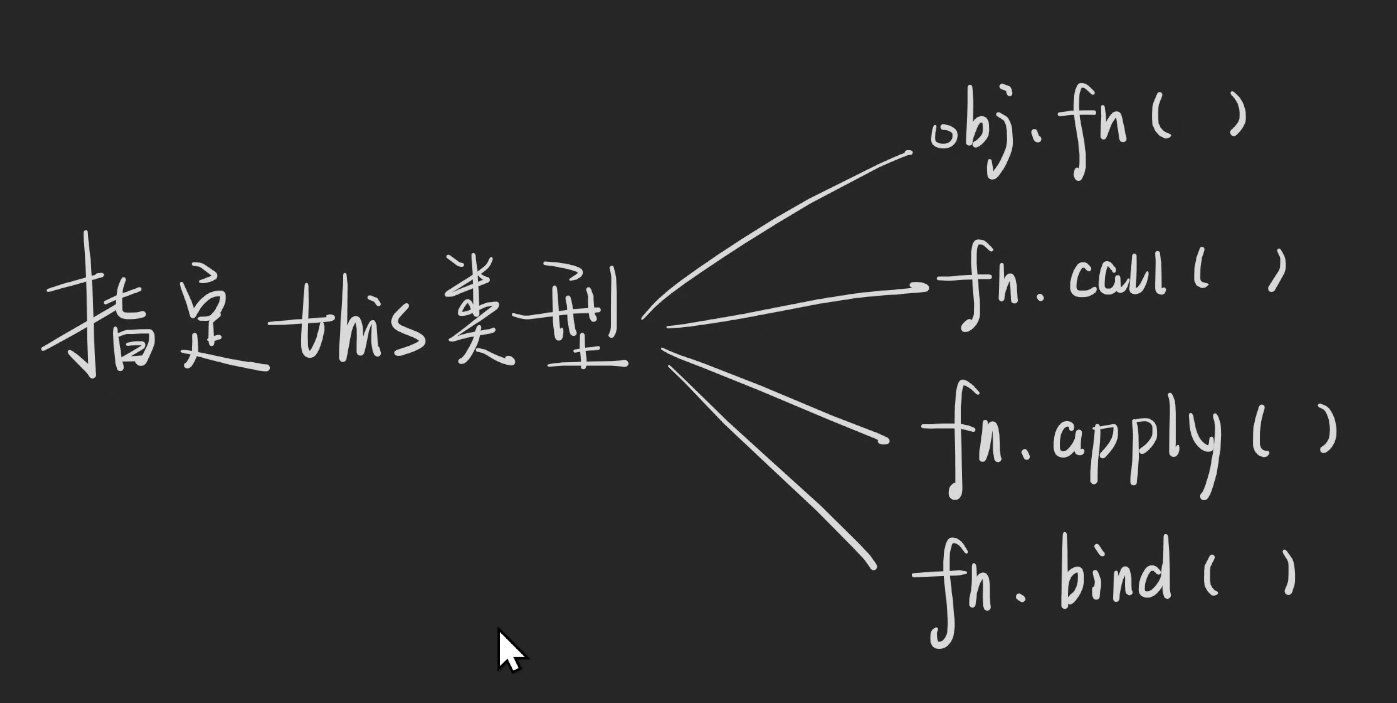
函数能够指定this,那么TS中如何指定类型,如下代码所示。TS中指定函数this的类型能不用就不用。
type Person = {
name: string
}
function f1(this: Person, n: number) {
console.log(n)
}
// f1(1)
// 1.person.f(1)
// 这种方法过于平凑
const p: Person & { f: typeof f1 } = {name: 'baizhe', f: f1}
p.f(1)
// 2. f.call(person,1)
const p2: Person = {name: 'baizhe'}
f1.call(p2, 1)
// 3. f.apply(person,[1])
const p3: Person = {name: 'baizhe'}
f1.apply(p3, [1])
// 4 f.bind(person)(1)
const p4: Person = {name: 'baizhe'}
const newF = f1.bind(p4)
newF(1)
// bind 用于部分赋值
// bind 补充内容
function x1(a:number,b:number,c:number) {
console.log(a+b+c)
}
const x2 = x1.bind(null) // null => this
const x3 = x2.bind(null,1) // 1 => a
const x4 = x3.bind(null,2) // 2 => b
const x5 = x4.bind( null, 3) // 3 => c
console.log(x5())
// 疑问!
// x1.call.bind(null,1)... 与 参数
- 剩余参数——用于参数长度不固定的情况。
// ... 与参数
function n1(...x: number[]) {
console.log(x)
}
n1(1)
n1(1,2)
n1(1,2,3)
function n2(a:number,...b:number[]) {
console.log(a,b)
}
n2(1)
n2(1,2)
n2(1,2,3)
// 用于参数长度不固定的情况- 展开参数与
as const,as const的内容具体可以见TS官网。数组或对象在结尾添加as const会添加上readonly只读属性。若是字符串类型的则不在扩展,也不会添加readonly属性。
// 展开参数案例1
function y(a:number, ...b:number[]){
y2.apply(null,b)
}
function y2(...a:number[]){
console.log(a)
}
// 展开参数与 as const案例2
function g(a:number,...b:number[]){
// let z = [1,2]
// 这里z TS会自动推断为number[],无法用于g2函数
// 解决方法:
// 1. 断言z为二元组 let z = [1,2] as [number,number]
// 2. 类型写死 let z:[number,number] = [1,2]
// 可以发现使用const定义const z = [1,2] 数组内还能在添加数字
// 3. 使用 as const
let z = [1,2] as const
// ^-- let z: readonly [1, 2]
// 自动类型推导
g2(...z)
}
function g2(a:number,b:number) {
console.log(a,b)
}
// 通过下面的例子可以看出 const 和 let 的区别
const consta = 1
type constA = typeof consta
// ^-- type 为 1
let leta = 1
type letA = typeof leta
// ^-- type 为 number
// 常量做类型推断往小的猜,变量做类型对端往大的猜- 参数对象析构
type Config = {
method: 'GET' | 'POST',
data?: unknown,
query?: {}
}
// 可以不传参数,接受参数对象析构赋值
request()
function request({method,data, ...rest}:Config = { method: 'GET'}){
console.log(method,data,rest)
}void 返回类型
若是函数先声明好返回类型为void,使用的时候可以return任何其他值,但他会被忽略。具体可以查看TS官网。
// 先声明好函数返回类型为void
type voidFunc = () => void;
const voidFunc1 = () => { return true }
const voidFunc2 = () => { return undefined }
const voidFunc3 = () => { return null }
const voidFunc4 = () => { }
// 不提前声明
function void1(): void {
return
}
function void2(): void {
return undefined
}
function void3(): void {}
function void4(): void {
return null
// ^--Type 'null' is not assignable to type 'void'
// 可以通过修改tsconfig.json的配置项 "strictNullChecks": false,
}